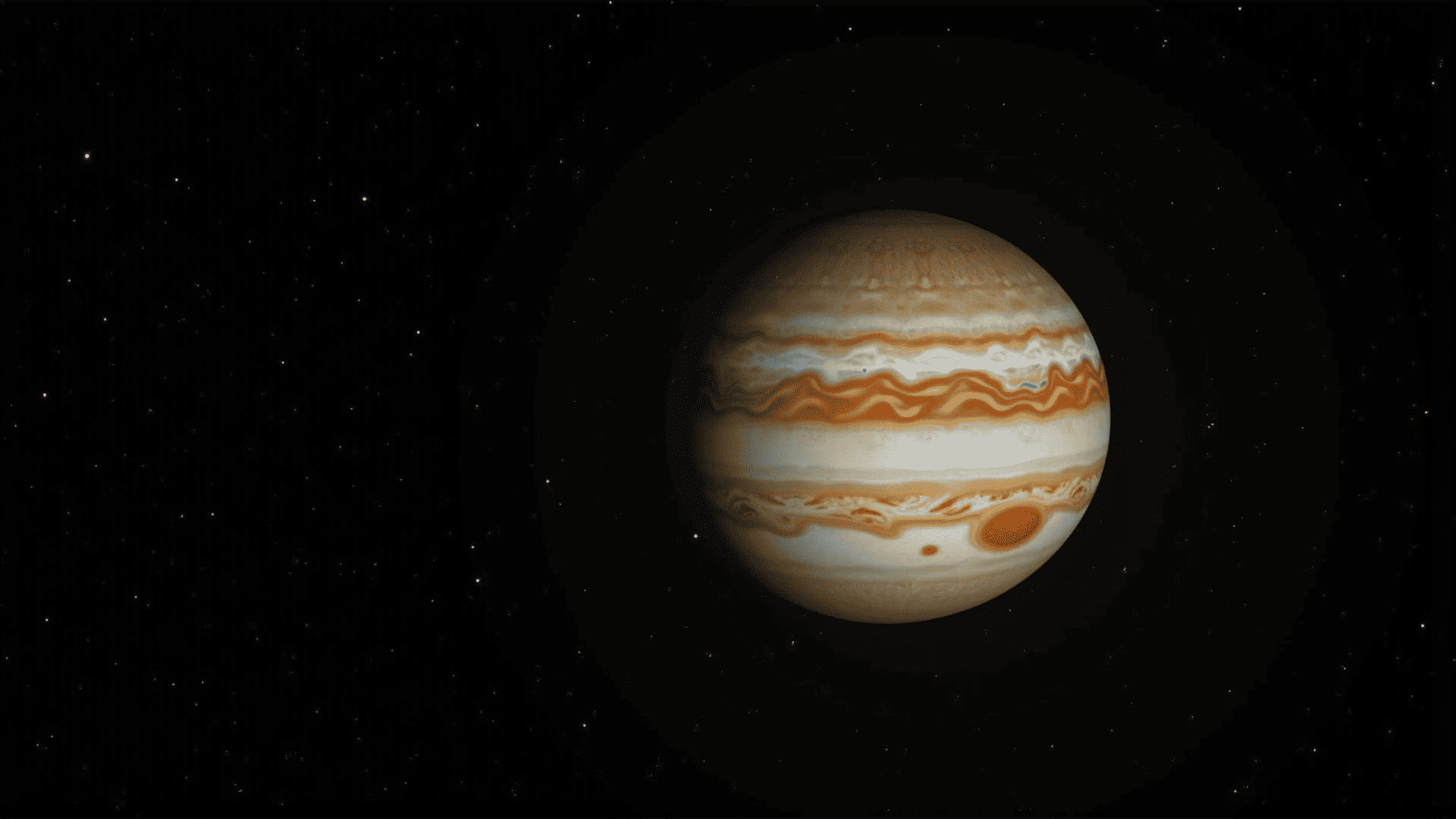
Jupiter, the largest of the planets in our solar system, is a breathtaking marvel of swirling clouds and immense beauty. As we delve into the mysteries of this giant planet, it becomes apparent why Jupiter has captivated astronomers and space enthusiasts alike for centuries.
The first thing that strikes the eye is Jupiter's vibrant and dynamic atmosphere. The planet's appearance is dominated by an array of colorful bands that stretch across its vast surface. These bands are created by the planet's fast rotation, which causes the clouds to whip around at incredible speeds, creating a tapestry of colors ranging from deep browns and reds to brilliant whites and yellows. Among these features is the Great Red Spot, a massive storm larger than Earth itself, that has raged for at least 350 years, offering a glimpse into the turbulent nature of Jupiter's atmosphere.
Jupiter's composition primarily consists of hydrogen and helium, making it a gas giant. It lacks a solid surface, with its gaseous atmosphere transitioning into a layer of metallic hydrogen deep within the planet. This unique structure leads to fascinating weather phenomena, including spectacular lightning storms and intense auroras near the poles, which have been captured in magnificent detail by spacecraft like NASA's Juno.
The photography of Jupiter reveals these intricate cloud patterns and phenomena in unprecedented detail. Through the lenses of space telescopes and missions, we can admire the intricate dance of its clouds, circled by swirling storms that are mesmerizing both in their beauty and their sheer scale.
Jupiter also serves as a focal point for understanding the broader cosmos. Its substantial gravitational pull influences both nearby planets and a retinue of moons, with the Galilean moons—Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto—being particularly noteworthy. Each of these moons possesses its own unique characteristics and potential clues about the possibilities of life beyond Earth, especially Europa, where a subsurface ocean lies beneath an icy crust.
In addition to its moons, Jupiter’s immense magnetic field, the largest in the solar system, extends millions of miles into space, capturing particles and forming a magnetosphere that offers a natural laboratory for studying magnetic and radiation phenomena.
As we continue our exploration, Jupiter remains a symbol of the mysteries that lie beyond Earth. It challenges and inspires us with its vastness and complexity, beckoning us to uncover the secrets hidden in its swirling clouds and deepen our understanding of the universe. The giant planet is not just a subject of scientific inquiry, but also a source of wonder, urging us to look up and dream about the celestial wonders that make up our solar system.